Hit enter to search or ESC to close
 Glass affects design, appearance, thermal performance and occupant comfort.
Glass affects design, appearance, thermal performance and occupant comfort.
The selection of the right glass is a crucial component of the design process. Windows are a fundamental and uniquely powerful design element of a home.
More than any other component, windows set the tone of your home by providing views, ventilation, daylight and a sense of spaciousness.
Window Glazing Types
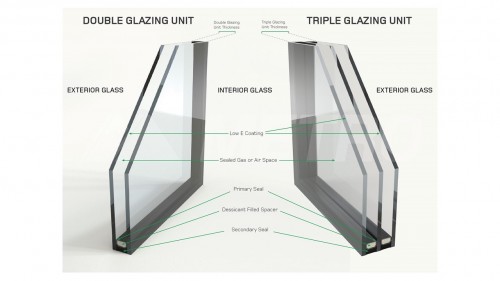
Glazing refers to the layers of glass that are sealed in a frame to make up a window. Traditionally, single glazing, with just one pane of glass in the frame, was used. Today, double glazing, with two layers of glass - or even triple glazing, with three layers - is increasingly popular because it reduces the amount of heat lost through windows and helps increase the energy efficiency of your home.
How double and triple glazing works
A single pane of glass offers very poor insulation, leading to a lot of heat lost through the glass in winter. Double or triple glazing traps air between two (or three) panes of glass, which by comparison to single glazing has twice the heat loss of double glazing.
Heat loss can be further reduced by coating one or more panes with transparent Low Emissivity (Low E) coating, which reflects the heat back into the room.
Thermally efficient window frames also help prevent heat loss and are ideally teamed with double or triple glazing. Other special glass treatments can be used in double or triple glazing for safety, security or fire resistance, or to match your decor.
Acoustic performance
Add in Laminated glass panel - optional sound stop upgrade
UV Reduction
• Add in Laminated glass panel
Solar heat
• Add a tint
• Use a Low - E
Single glazing
A single pane of glass provides very poor insulation because glass is a good conductor of heat. Much of the heat in your room literally goes out the window.
Double glazing
Install double glazing and you have a layer of air trapped between two panes of glass. Because air is a poor conductor of heat, much less heat is lost through the window. If the inside of one pane has Low E coating, even less heat is lost, because the coating reflects heat back into the room.
Triple glazing
Install triple glazing and you have an additional layer of air trapped between each of the three panes of glass. Because air is a poor conductor of heat, much less heat is lost through the window.
Low-E Coating, Argon Gas Filled, Thermal Spacer
More options are now available for your glass choice. If the inside of one pane has Low E coating, even less heat is lost, because the coating reflects heat back into the room. By the same token, adding Argon gas to the internal cavity of the IGU will help with the thermal performance. And changing out the aluminium spacer for a thermal spacer will again increase the thermal performance of the glass unit.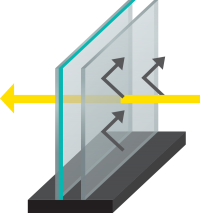
Why choose double or triple glazing?
- Reduces condensation foaming on Glass
- Keeps you warm in winter, cool in summer
- Reduces energy bills
- Replaces thermal drapes
- Reduces noise
- Requires minimal maintenance
- Improves security
- Upgrades and adds value to your home
In double glazing, the air between the two panes of glass acts like an insulating ‘blanket’ - storing heat and releasing it slowly
to help you control the temperature of your home. As the name suggests, triple glazing has three panes of glass, adding an
extra insulating layer for additional warmth. It is most often used in colder climates, such as in the South Island. For new builds, double or triple glazing can help you meet the requirements for energy efficiency in line with The New Zealand Building Code requirement for new residential construction.
CHOOSING THE RIGHT DOUBLE OR TRIPLE GLAZING
For most homes in New Zealand, double glazing will be enough to significantly improve comfort and warmth and increase energy efficiency. Triple glazing is likely to be of most benefit to people in the coldest parts of the country or where noise pollution is an issue.
Thermal performance
Thermal performance measures the effectiveness of glazing in reducing heat loss. This measure is called a U value and can
provide a useful guide to the difference double or triple glazing could make in your home.
The higher the U value, the less energy efficient the window is, meaning more heat is lost. The U value of a single-glazed window can be 5 or higher, while a triple-glazed window could have a U
value of less than 1.
This chart compares single glazing with double glazing (with and without a Low E coating) and shows just how effective these
different forms of insulation can be.
Another useful measure of energy efficiency is our WEERS (Window Energy Efficiency Rating System) which rates the actual
energy efficiency of the windows you purchase for your home.
- CDG = Clear Double Glazed
- A LE DG = Argon Filled, Low-E coating, Double Glazed
KEY FACTS
- Single, double or triple glazing refers to the number of panes of glass that are sealed in a frame to make up a window.
- Double or triple glazing has a layer of insulating air, or other gas, between panes that acts in a similar way to a fibreglass batt in a wall. It reduces heat loss from windows and increases comfort and warmth.
- Other benefits of double or triple glazing can include lower energy bills and reduced noise.
- A Low-E glass coating can further boost the benefits of double or triple glazing.
- Thermal performance measures effectiveness of glazing and shows the difference double and triple glazing can make to improving the energy efficiency of your home.


























